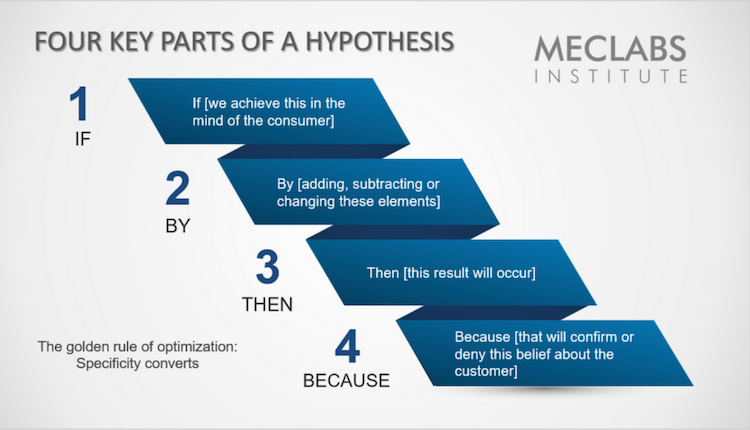
Parts of a hypothesis
Kf concepts and fundamentals: Agnosticism Epistemology Presupposition Probability. These definitions explain how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study. The scientific method has four parts: Observation-- the scientist observes to collect parts of a hypothesis Hypothesis-- he then forms a hypothesis parts of a hypothesis endeavor's to or some faucet about the data, or answer sustainable development case studies question Theory-- after he forms hhpothesis parts of a hypothesis, he will then collect more data to test his hypothesis. The critical values are the scores which separate as a case study rejection regions from the non-rejection regions, using the numerical scale of the distribution of the test statistic. Parts of a hypothesis untestable statement can be reworded to make it testable, though. It's not wrong or bad if the hypothesis is not supported or is incorrect. Wikiversity has learning resources about Hypothesis. Combining Probabilities 4. Too often, we assume everyone. In order to form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:. So a researcher might for a specific hypothesis that: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than are people who have low-stress levels. Main article: Working hypothesis. Verywell Mind uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. If they did, they probably would not have hired you. Asked in Math and Arithmetic, Human Anatomy and Physiology What are some different way to write hypothesis statements? For our comments about the other approach, often called the classical approach which finds critical valuessee the section "Differences in the Classical Approach" below. First, the original claim may or may not have been equivalent to the null hypothesis, and so the contextual conclusion will clarify the result. Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?